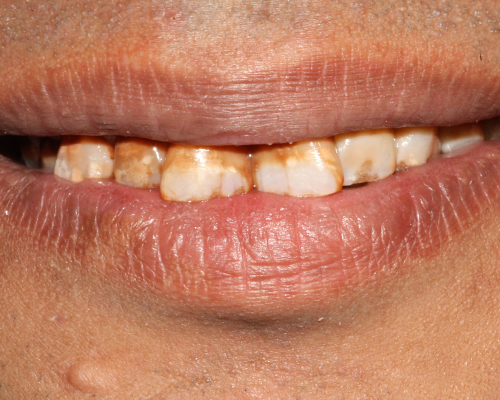
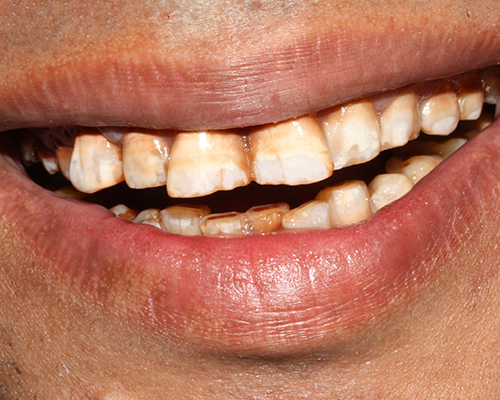
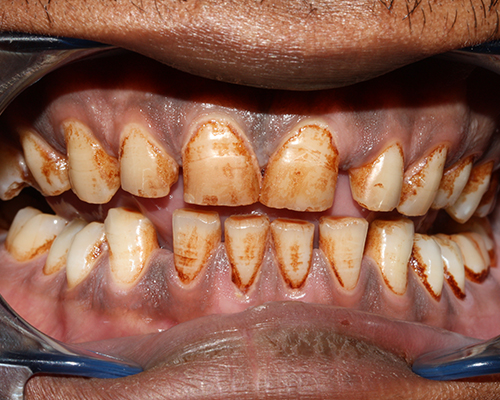
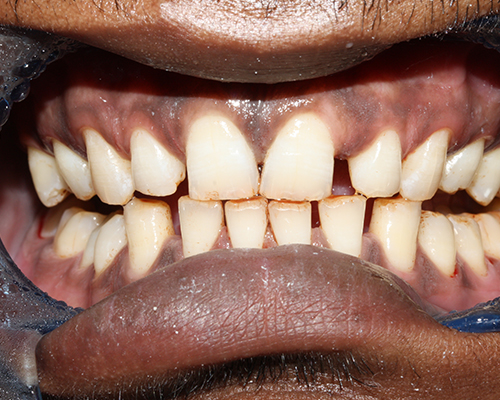
Tooth whitening
Teeth whitening is a popular cosmetic dental procedure aimed at lightening the color of teeth and removing stains and discoloration. Here are the main types of teeth whitening treatments:
Types of Teeth Whitening
1. In-Office Teeth Whitening
- Procedure: Performed by a dentist, this method uses a high-concentration bleaching agent, usually hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, often activated by a special light or laser.
- Duration: Typically completed in one visit, lasting about 60 to 90 minutes.
- Results: Immediate and can lighten teeth several shades in a single session.
- Cost: Higher compared to at-home treatments, but offers professional supervision and rapid results.
2. At-Home Teeth Whitening Kits
- Dentist-Supervised Kits: Custom trays are made by a dentist, and patients use a lower-concentration bleaching gel at home.
- Procedure: Patients wear the trays filled with the bleaching gel for a specified period each day, usually for a few hours or overnight, over one to two weeks.
- Results: Effective and can achieve similar results to in-office treatments over a longer period.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products: These include whitening strips, gels, pens, and trays available at pharmacies and stores.
- Procedure: Follow the instructions on the product; typically, these products have a lower concentration of bleaching agents compared to professional treatments.
- Results: Vary widely, often less effective and slower than professional treatments.
3. Whitening Toothpaste and Rinses
- Procedure: These products contain mild abrasives or low concentrations of bleaching agents to remove surface stains.
- Results: Gradual and subtle, primarily maintaining the whiteness achieved by other whitening methods.
Considerations
1. Effectiveness
- Results depend on the initial color of the teeth, the type and concentration of the bleaching agent, and the duration of treatment.
- Not all discolorations respond equally to whitening; yellowish teeth typically bleach well, while brownish or grayish hues might be less responsive.
2. Safety and Sensitivity
- Professional supervision reduces the risk of over-bleaching and gum irritation.
- Common side effects include tooth sensitivity and gum irritation, usually temporary.
- Using desensitizing toothpaste and following dentist recommendations can help manage sensitivity.
3. Longevity
- The effects of teeth whitening are not permanent. Stains can reoccur due to habits like smoking, and consumption of staining foods and drinks (coffee, tea, red wine).
- Touch-up treatments and good oral hygiene can prolong the whitening effects.
4. Suitability
- Not everyone is a candidate for teeth whitening. It's not recommended for pregnant or nursing women, children under a certain age, and individuals with certain dental conditions (e.g., cavities, gum disease).
- Restorations like crowns, veneers, or fillings do not whiten and might need replacement to match the bleached teeth.
Steps to Maintain Whitened Teeth
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily, floss daily, and use mouthwash.
- Avoid Staining Foods and Drinks: Limit intake of coffee, tea, red wine, and colored sodas.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Professional cleanings can help maintain the results.
- Use a Straw: When drinking staining beverages to minimize contact with teeth.
Teeth whitening can significantly enhance your smile's appearance, but it's important to choose the right method and follow professional advice to ensure safety and effectiveness.