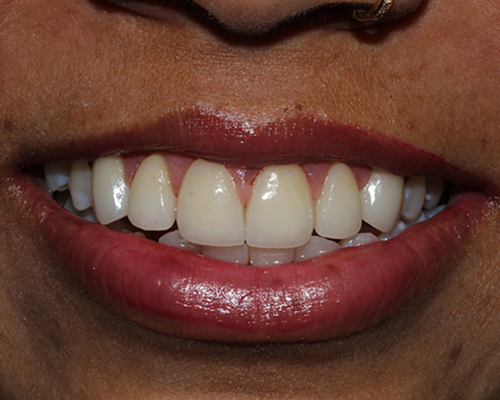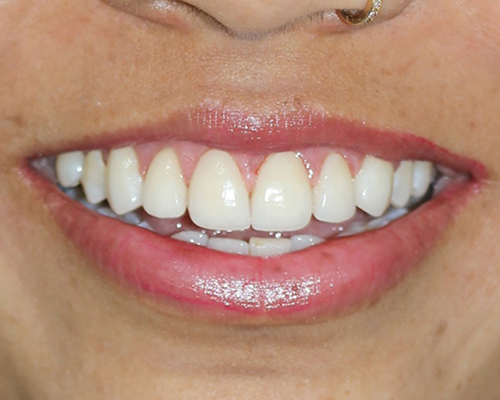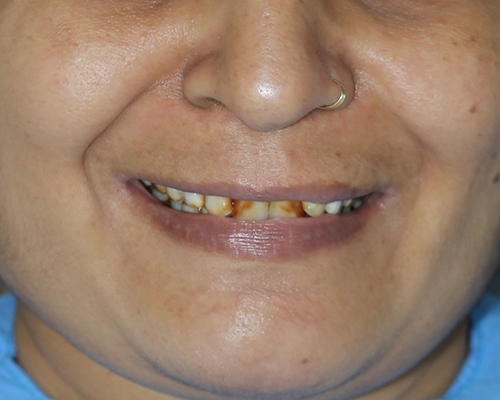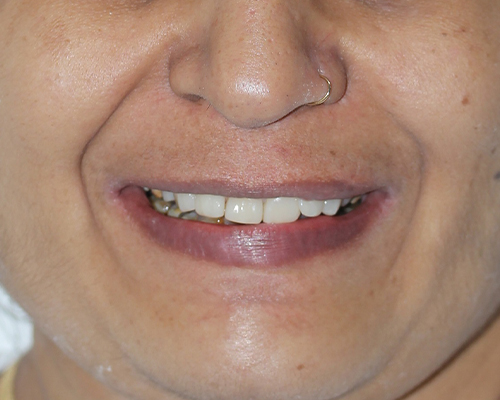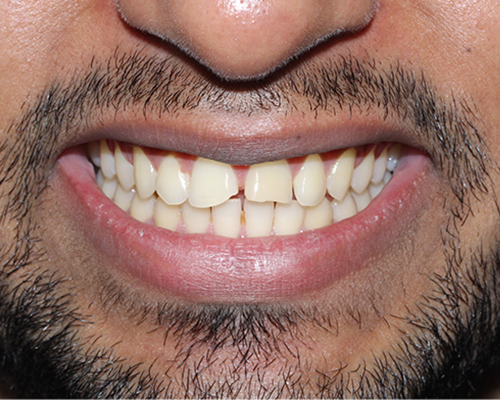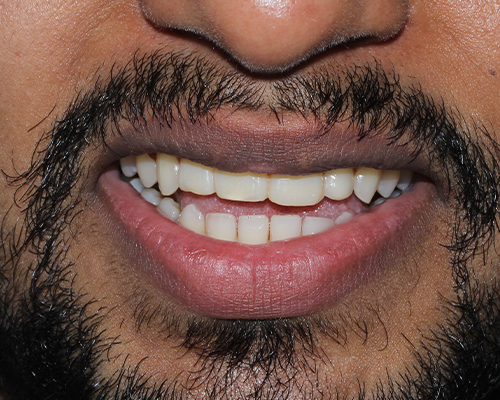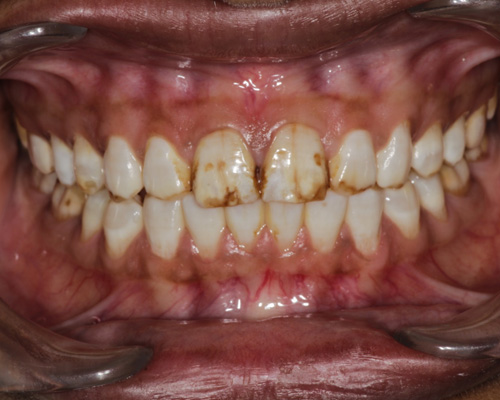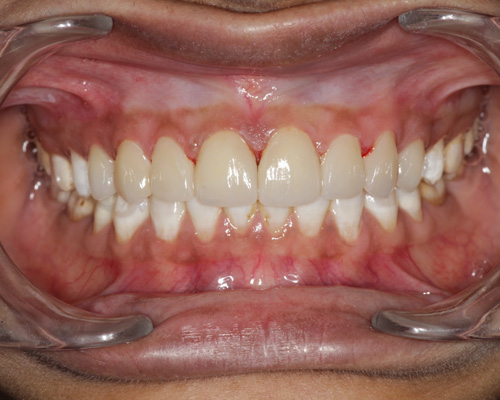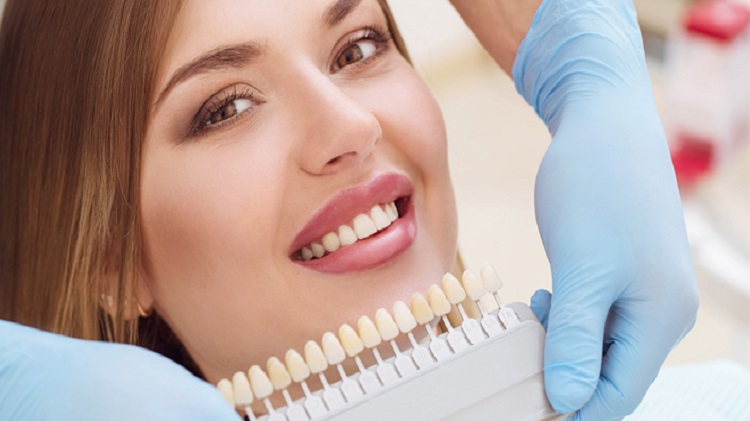
Laminates & Veneers
Laminates and veneers are both popular cosmetic dental treatments used to improve the appearance of teeth. While they serve similar purposes, there are differences between the two.
Veneers
Definition: Veneers are thin shells, typically made of porcelain or composite resin, that are custom-made to cover the front surface of the teeth.
Purpose: They are used to improve the appearance of teeth that are discolored, chipped, worn down, misaligned, uneven, or have gaps between them.
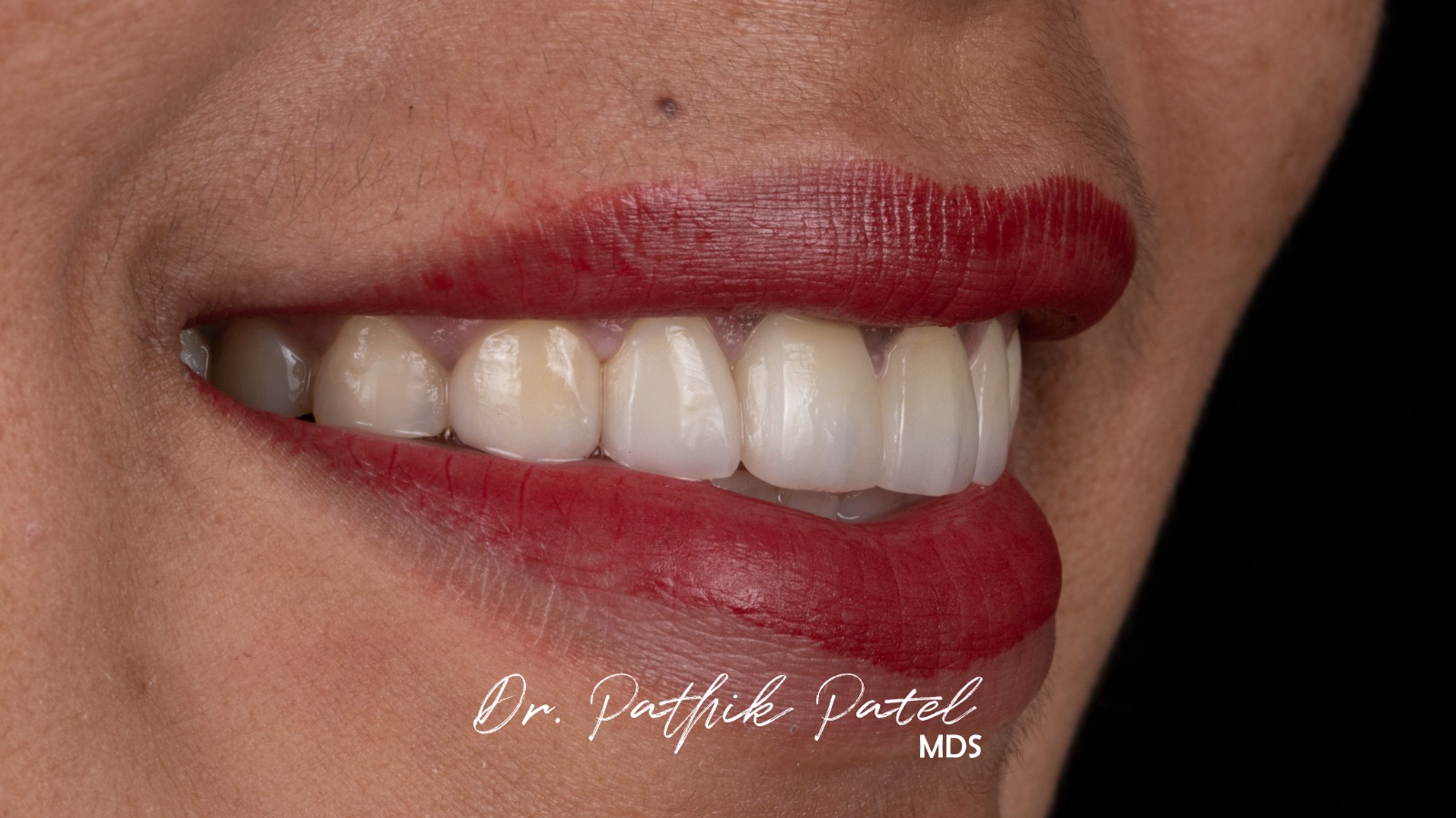
Process
- Consultation and Planning: The dentist evaluates the patient’s teeth and discusses the desired outcome.
- Preparation: A small amount of enamel (usually less than a millimeter) is removed from the tooth surface to accommodate the veneer.
- Impressions: An impression of the prepared tooth is taken and sent to a dental laboratory where the veneers are custom-made.
- Bonding: The dentist fits the veneer on the tooth to check its fit and color. After adjustments, the veneer is bonded to the tooth with a special adhesive.
Advantages
- Natural appearance
- Stain resistance, especially with porcelain veneers
- Durability, with porcelain veneers lasting 10-15 years with proper care
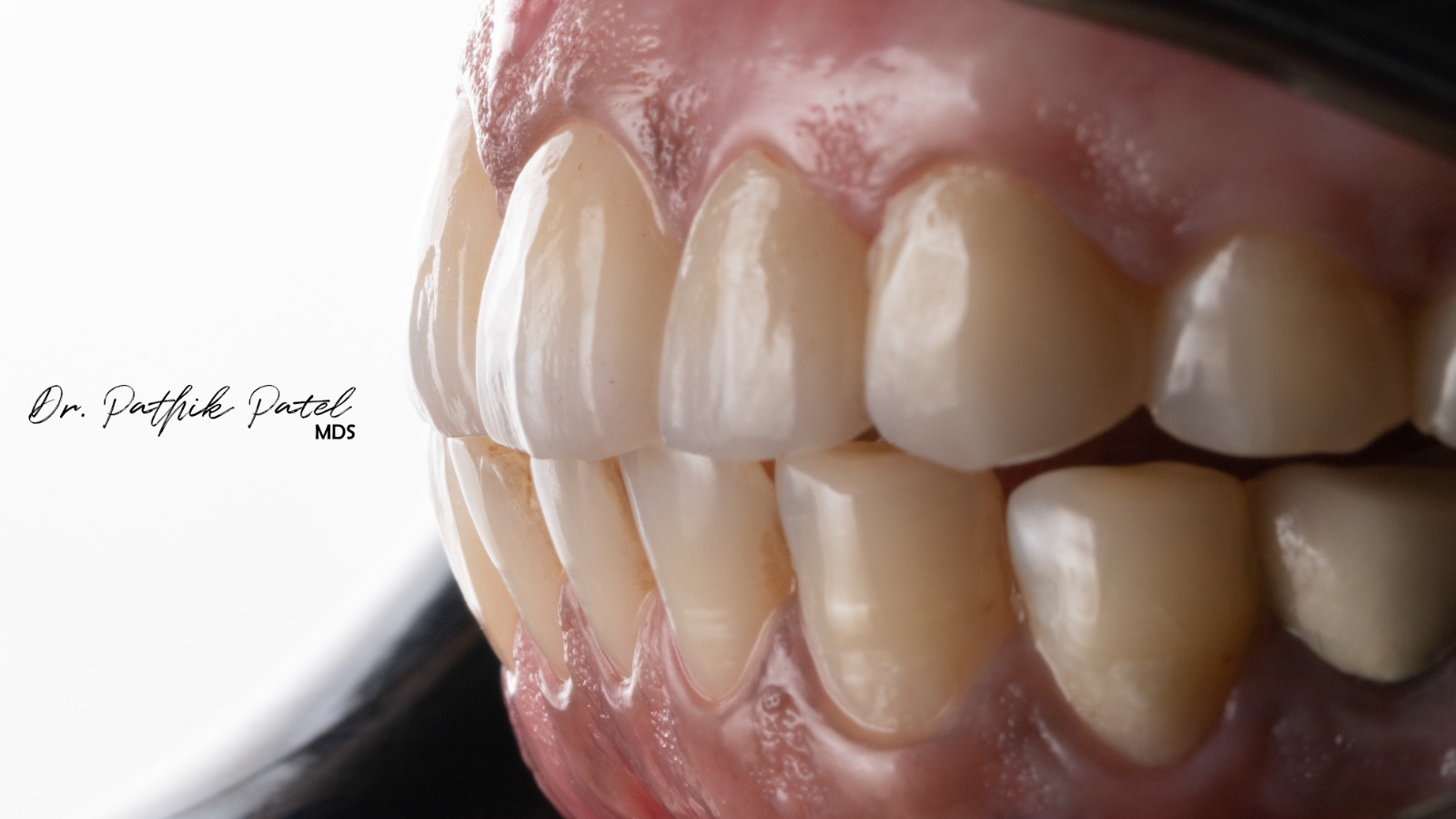
Disadvantages
- Irreversible procedure due to enamel removal
- Higher cost compared to other cosmetic options
Laminates
Definition: Dental laminates are a type of veneer but typically refer to ultra-thin veneers that require minimal to no enamel removal.
Purpose: Similar to veneers, laminates are used for cosmetic enhancements like covering stains, chips, or gaps, and improving the overall aesthetics of the smile.
Process
- Consultation and Planning: The dentist assesses the teeth and discusses the patient’s goals.
- Minimal Preparation: Little to no enamel is removed, preserving more of the natural tooth structure.
- Impressions: An impression is taken to create the custom laminates.
- Bonding: The laminates are tried on for fit and color and then bonded to the teeth using a special adhesive.
Advantages
- Minimal or no removal of tooth enamel
- Natural look and feel
- Quick procedure with less discomfort
Disadvantages
- May not be suitable for teeth with significant damage or alignment issues
- Less durable than traditional porcelain veneers and might require more frequent replacement
Comparison
Thickness
Veneers: Typically thicker than laminates, providing more coverage and durability.
Laminates: Ultra-thin, usually less invasive.
Durability
Veneers: Generally more durable and long-lasting.
Laminates: Less durable, may need more frequent replacements.
Invasiveness
Veneers: Require more tooth preparation, which is irreversible.
Laminates: Minimal to no tooth preparation, preserving more of the natural tooth.
Suitability
Veneers: Suitable for a wide range of cosmetic issues, including significant discoloration and damage.
Laminates: Best for minor cosmetic enhancements and patients looking for a less invasive option.
Both laminates and veneers can provide significant improvements in the appearance of your smile. The choice between the two depends on the specific dental issues, patient preferences, and recommendations from the dentist.